Generator Overview
The Generator allows users to define and configure models along with their fields for a Laravel application. Users can customize the model name, fields, relationships, and other attributes that will be used to generate the backend API, database, and frontend CMS.
UI Preview
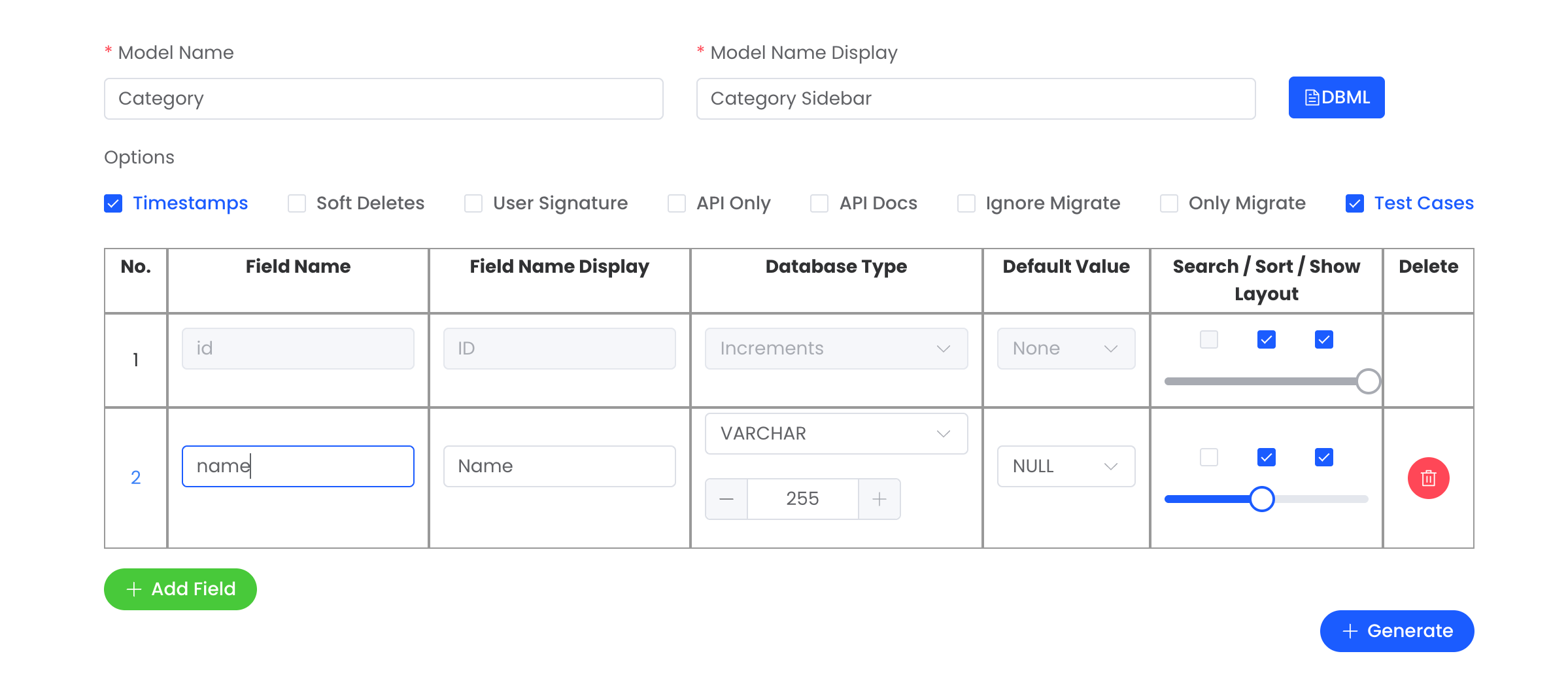
Model Configuration
| Field | Description | Default | Example | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Model Name | Defines the name of the model | Category | Required | |
Model Name Display | Display name in menu bar | Category Sidebar | Required |
Options
| Field | Description | Default | Example | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Timestamps | Automatically adds created_at and updated_at columns to the table. | Checked | Optional | |
Soft Deletes | Adds support for soft deletion (adds a deleted_at column). | Checked | Optional | |
User Signature | Adds created_by and updated_by columns to track who created/updated records. | UnChecked | Optional | |
API Only | Only generate the API. | UnChecked | Optional | |
API Docs | Generate docs for the API. Learn more | UnChecked | Optional | |
Ignore Migrate | Skips running database migrations. | UnChecked | Optional | |
Only Migrate | Only generate migration and Model. | UnChecked | Optional | |
Test Cases | Generates test cases for the model and related services. | Checked | Optional |
If you enable API Docs
API Docs Required
Install the Scribe package first:
composer require knuckleswtf/scribeReference config (Optional):
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
use Knuckles\Scribe\Extracting\Strategies;
return [
// The HTML <title> for the generated documentation. If this is empty, Scribe will infer it from config('app.name').
'title' => 'LaraJS API Documentation',
// A short description of your API. Will be included in the docs webpage, Postman collection and OpenAPI spec.
'description' => '',
// The base URL displayed in the docs. If this is empty, Scribe will use the value of config('app.url') at generation time.
// If you're using `laravel` type, you can set this to a dynamic string, like '{{ config("app.tenant_url") }}' to get a dynamic base URL.
'base_url' => null,
'routes' => [
[
// Routes that match these conditions will be included in the docs
'match' => [
// Match only routes whose paths match this pattern (use * as a wildcard to match any characters). Example: 'users/*'.
'prefixes' => ['api/*'],
// Match only routes whose domains match this pattern (use * as a wildcard to match any characters). Example: 'api.*'.
'domains' => ['*'],
// [Dingo router only] Match only routes registered under this version. Wildcards are NOT supported.
'versions' => ['v1'],
],
// Include these routes even if they did not match the rules above.
'include' => [
// 'users.index', 'POST /new', '/auth/*'
],
// Exclude these routes even if they matched the rules above.
'exclude' => ['api/v1/generators*'],
],
],
// The type of documentation output to generate.
// - "static" will generate a static HTMl page in the /public/docs folder,
// - "laravel" will generate the documentation as a Blade view, so you can add routing and authentication.
// - "external_static" and "external_laravel" do the same as above, but generate a basic template,
// passing the OpenAPI spec as a URL, allowing you to easily use the docs with an external generator
'type' => 'external_static',
// See https://scribe.knuckles.wtf/laravel/reference/config#theme for supported options
'theme' => 'elements',
'static' => [
// HTML documentation, assets and Postman collection will be generated to this folder.
// Source Markdown will still be in resources/docs.
'output_path' => 'public/docs',
],
'laravel' => [
// Whether to automatically create a docs endpoint for you to view your generated docs.
// If this is false, you can still set up routing manually.
'add_routes' => false,
// URL path to use for the docs endpoint (if `add_routes` is true).
// By default, `/docs` opens the HTML page, `/docs.postman` opens the Postman collection, and `/docs.openapi` the OpenAPI spec.
'docs_url' => '/docs',
// Directory within `public` in which to store CSS and JS assets.
// By default, assets are stored in `public/vendor/scribe`.
// If set, assets will be stored in `public/{{assets_directory}}`
'assets_directory' => null,
// Middleware to attach to the docs endpoint (if `add_routes` is true).
'middleware' => [],
],
'external' => [
'html_attributes' => [],
],
'try_it_out' => [
// Add a Try It Out button to your endpoints so consumers can test endpoints right from their browser.
// Don't forget to enable CORS headers for your endpoints.
'enabled' => true,
// The base URL for the API tester to use (for example, you can set this to your staging URL).
// Leave as null to use the current app URL when generating (config("app.url")).
'base_url' => null,
// [Laravel Sanctum] Fetch a CSRF token before each request, and add it as an X-XSRF-TOKEN header.
'use_csrf' => true,
// The URL to fetch the CSRF token from (if `use_csrf` is true).
'csrf_url' => '/sanctum/csrf-cookie',
],
// How is your API authenticated? This information will be used in the displayed docs, generated examples and response calls.
'auth' => [
// Set this to true if ANY endpoints in your API use authentication.
'enabled' => true,
// Set this to true if your API should be authenticated by default. If so, you must also set `enabled` (above) to true.
// You can then use @unauthenticated or @authenticated on individual endpoints to change their status from the default.
'default' => false,
// Where is the auth value meant to be sent in a request?
// Options: query, body, basic, bearer, header (for custom header)
'in' => 'bearer',
// The name of the auth parameter (eg token, key, apiKey) or header (eg Authorization, Api-Key).
'name' => 'Authorization',
// The value of the parameter to be used by Scribe to authenticate response calls.
// This will NOT be included in the generated documentation. If empty, Scribe will use a random value.
'use_value' => env('SCRIBE_AUTH_KEY'),
// Placeholder your users will see for the auth parameter in the example requests.
// Set this to null if you want Scribe to use a random value as placeholder instead.
'placeholder' => '{ACCESS_TOKEN}',
// Any extra authentication-related info for your users. Markdown and HTML are supported.
'extra_info' => 'You can retrieve your token by visiting your dashboard and clicking <b>Generate API token</b>.',
],
// Text to place in the "Introduction" section, right after the `description`. Markdown and HTML are supported.
'intro_text' => <<<'INTRO'
This documentation aims to provide all the information you need to work with our API.
<aside>As you scroll, you'll see code examples for working with the API in different programming languages in the dark area to the right (or as part of the content on mobile).
You can switch the language used with the tabs at the top right (or from the nav menu at the top left on mobile).</aside>
INTRO
,
// Example requests for each endpoint will be shown in each of these languages.
// Supported options are: bash, javascript, php, python
// To add a language of your own, see https://scribe.knuckles.wtf/laravel/advanced/example-requests
'example_languages' => ['bash', 'javascript'],
// Generate a Postman collection (v2.1.0) in addition to HTML docs.
// For 'static' docs, the collection will be generated to public/docs/collection.json.
// For 'laravel' docs, it will be generated to storage/app/scribe/collection.json.
// Setting `laravel.add_routes` to true (above) will also add a route for the collection.
'postman' => [
'enabled' => true,
'overrides' => [
// 'info.version' => '2.0.0',
],
],
// Generate an OpenAPI spec (v3.0.1) in addition to docs webpage.
// For 'static' docs, the collection will be generated to public/docs/openapi.yaml.
// For 'laravel' docs, it will be generated to storage/app/scribe/openapi.yaml.
// Setting `laravel.add_routes` to true (above) will also add a route for the spec.
'openapi' => [
'enabled' => true,
'overrides' => [
// 'info.version' => '2.0.0',
],
],
'groups' => [
// Endpoints which don't have a @group will be placed in this default group.
'default' => 'Endpoints',
// By default, Scribe will sort groups alphabetically, and endpoints in the order their routes are defined.
// You can override this by listing the groups, subgroups and endpoints here in the order you want them.
// See https://scribe.knuckles.wtf/blog/laravel-v4#easier-sorting and https://scribe.knuckles.wtf/laravel/reference/config#order for details
'order' => [],
],
// Custom logo path. This will be used as the value of the src attribute for the <img> tag,
// so make sure it points to an accessible URL or path. Set to false to not use a logo.
// For example, if your logo is in public/img:
// - 'logo' => '../img/logo.png' // for `static` type (output folder is public/docs)
// - 'logo' => 'img/logo.png' // for `laravel` type
'logo' => '../images/logo.png',
// Customize the "Last updated" value displayed in the docs by specifying tokens and formats.
// Examples:
// - {date:F j Y} => March 28, 2022
// - {git:short} => Short hash of the last Git commit
// Available tokens are `{date:<format>}` and `{git:<format>}`.
// The format you pass to `date` will be passed to PHP's `date()` function.
// The format you pass to `git` can be either "short" or "long".
'last_updated' => 'Last updated: {date:F j, Y}',
'examples' => [
// Set this to any number (eg. 1234) to generate the same example values for parameters on each run,
'faker_seed' => null,
// With API resources and transformers, Scribe tries to generate example models to use in your API responses.
// By default, Scribe will try the model's factory, and if that fails, try fetching the first from the database.
// You can reorder or remove strategies here.
'models_source' => ['factoryCreate', 'factoryMake', 'databaseFirst'],
],
// The strategies Scribe will use to extract information about your routes at each stage.
// If you create or install a custom strategy, add it here.
'strategies' => [
'metadata' => [
Strategies\Metadata\GetFromDocBlocks::class,
Strategies\Metadata\GetFromMetadataAttributes::class,
],
'urlParameters' => [
Strategies\UrlParameters\GetFromLaravelAPI::class,
Strategies\UrlParameters\GetFromUrlParamAttribute::class,
Strategies\UrlParameters\GetFromUrlParamTag::class,
],
'queryParameters' => [
Strategies\QueryParameters\GetFromFormRequest::class,
Strategies\QueryParameters\GetFromInlineValidator::class,
Strategies\QueryParameters\GetFromQueryParamAttribute::class,
Strategies\QueryParameters\GetFromQueryParamTag::class,
],
'headers' => [
Strategies\Headers\GetFromHeaderAttribute::class,
Strategies\Headers\GetFromHeaderTag::class,
[
'override',
[
'Content-Type' => 'application/json',
'Accept' => 'application/json',
],
],
],
'bodyParameters' => [
Strategies\BodyParameters\GetFromFormRequest::class,
Strategies\BodyParameters\GetFromInlineValidator::class,
Strategies\BodyParameters\GetFromBodyParamAttribute::class,
Strategies\BodyParameters\GetFromBodyParamTag::class,
],
'responses' => [
Strategies\Responses\UseResponseAttributes::class,
Strategies\Responses\UseTransformerTags::class,
Strategies\Responses\UseApiResourceTags::class,
Strategies\Responses\UseResponseTag::class,
Strategies\Responses\UseResponseFileTag::class,
],
'responseFields' => [
Strategies\ResponseFields\GetFromResponseFieldAttribute::class,
Strategies\ResponseFields\GetFromResponseFieldTag::class,
],
],
// For response calls, API resource responses and transformer responses,
// Scribe will try to start database transactions, so no changes are persisted to your database.
// Tell Scribe which connections should be transacted here. If you only use one db connection, you can leave this as is.
'database_connections_to_transact' => [config('database.default')],
'fractal' => [
// If you are using a custom serializer with league/fractal, you can specify it here.
'serializer' => null,
],
'routeMatcher' => \Knuckles\Scribe\Matching\RouteMatcher::class,
];Fields Configuration
| Field | Description | Default | Example | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Field Name | The name of the field in the database. | name | Required | |
Field Name Display | Display name for the field in the user interface. | Name | Required | |
Field Option | Setting unique, indexing, and adding comments. | Optional | ||
Database Type | The type of the field in the database (e.g., Increments, VARCHAR, LONGTEXT). | VARCHAR(255) | VARCHAR(255) | Required |
Default Value | The default value for this field if none is provided. | NULL | Required | |
Search/Sort/Show/Layout | On/Off search, sort, and show in the table. The column layout can be adjusted to a value between 1 and 24. | Optional | ||
Delete | Option to delete the field from the configuration. |
🔧 Field Option
| Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
Unique | Ensures the field value is unique across all records in the database. | Enabled for email field to ensure unique emails. |
Index | Creates an index on the field to optimize database query performance. | Enabled for status field to improve search speed. |
Comment | Adds a comment for the field in the database, useful for documentation or clarification purposes. | Indicates if the category is active or inactive. |
UI Preview
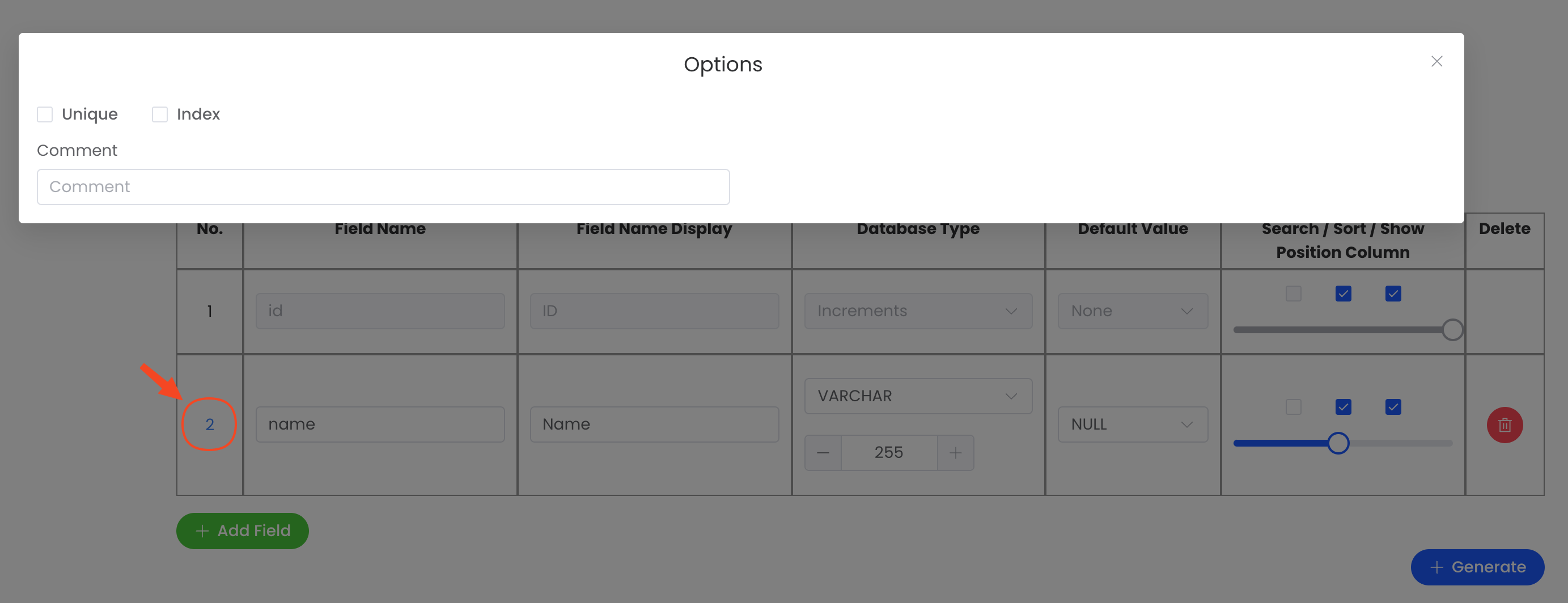
📦 Database Type
🗄️ Database
| Database Type | Display Name | Search | Sort | Show |
|---|---|---|---|---|
increments | Increments | 🚫 | ✅ | ✅ |
integer | INTEGER | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
unsignedInteger | UNSIGNED INTEGER | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
tinyInteger | TINYINT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
unsignedTinyInteger | UNSIGNED TINYINT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
smallInteger | SMALLINT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
unsignedSmallInteger | UNSIGNED SMALLINT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
mediumInteger | MEDIUMINT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
unsignedMediumInteger | UNSIGNED MEDIUMINT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
bigInteger | BIGINT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
unsignedBigInteger | UNSIGNED BIGINT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
float | FLOAT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
double | DOUBLE | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
decimal | DECIMAL | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
boolean | BOOLEAN | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
date | DATE | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
dateTime | DATETIME | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
timestamp | TIMESTAMP | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
time | TIME | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
year | YEAR | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
char | CHAR | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
string | VARCHAR | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
tinyText | TINYTEXT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
mediumText | MEDIUMTEXT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
text | TEXT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
longText | LONGTEXT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
enum | ENUM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
json | JSON | 🚫 | 🚫 | ✅ |
jsonb | JSONB | 🚫 | 🚫 | ✅ |
| Relationship Types | ||||
hasOne | hasOne | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
hasMany | hasMany | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
📝 Form
Each Database Type will feature a distinct UI, with our focus centered on utilizing the Element Plus components.
| Database Type | UI Preview |
|---|---|
INTEGER, UNSIGNED INTEGER, TINYINT, UNSIGNED TINYINT, SMALLINT, UNSIGNED SMALLINT, MEDIUMINT, UNSIGNED MEDIUMINT, BIGINT, UNSIGNED BIGINT, FLOAT, DOUBLE, DECIMAL | |
BOOLEAN | |
DATE | 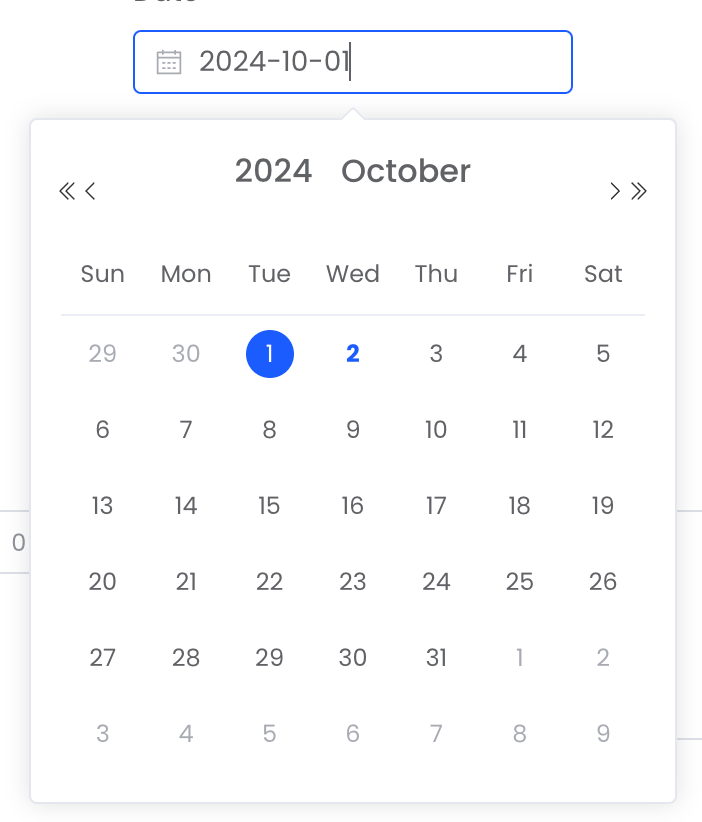 |
DATETIME, TIMESTAMP | 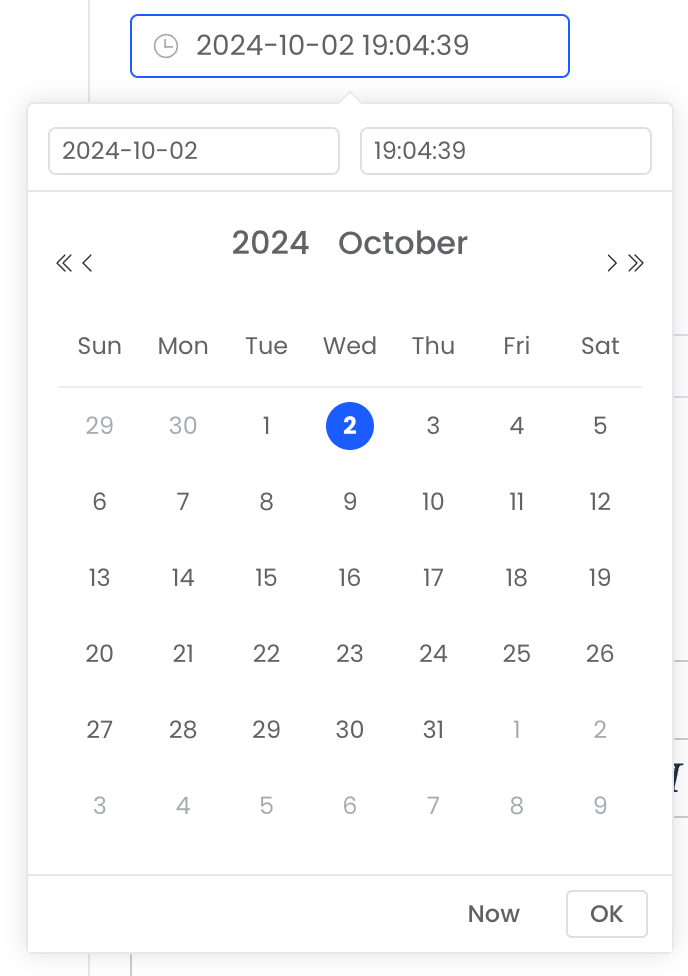 |
TIME | 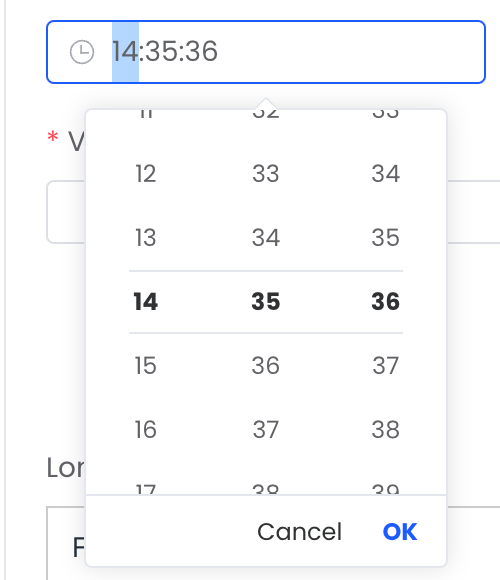 |
YEAR | 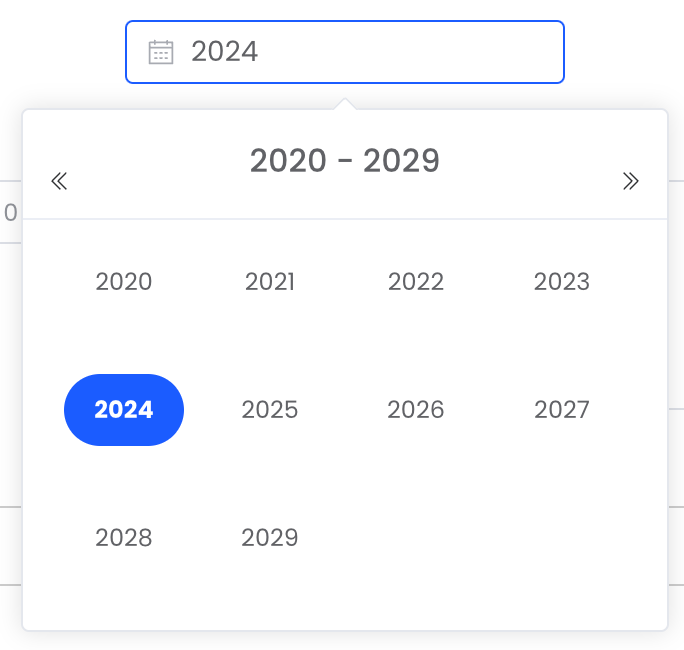 |
CHAR, VARCHAR |  |
TINYTEXT, MEDIUMTEXT, TEXT |  |
LONGTEXT |  |
ENUM |  |
JSON, JSONB |  |
Relationships
There are two ways to create relationships in our system:
Example:
Post → belongs to → Category
Category → has many → Post
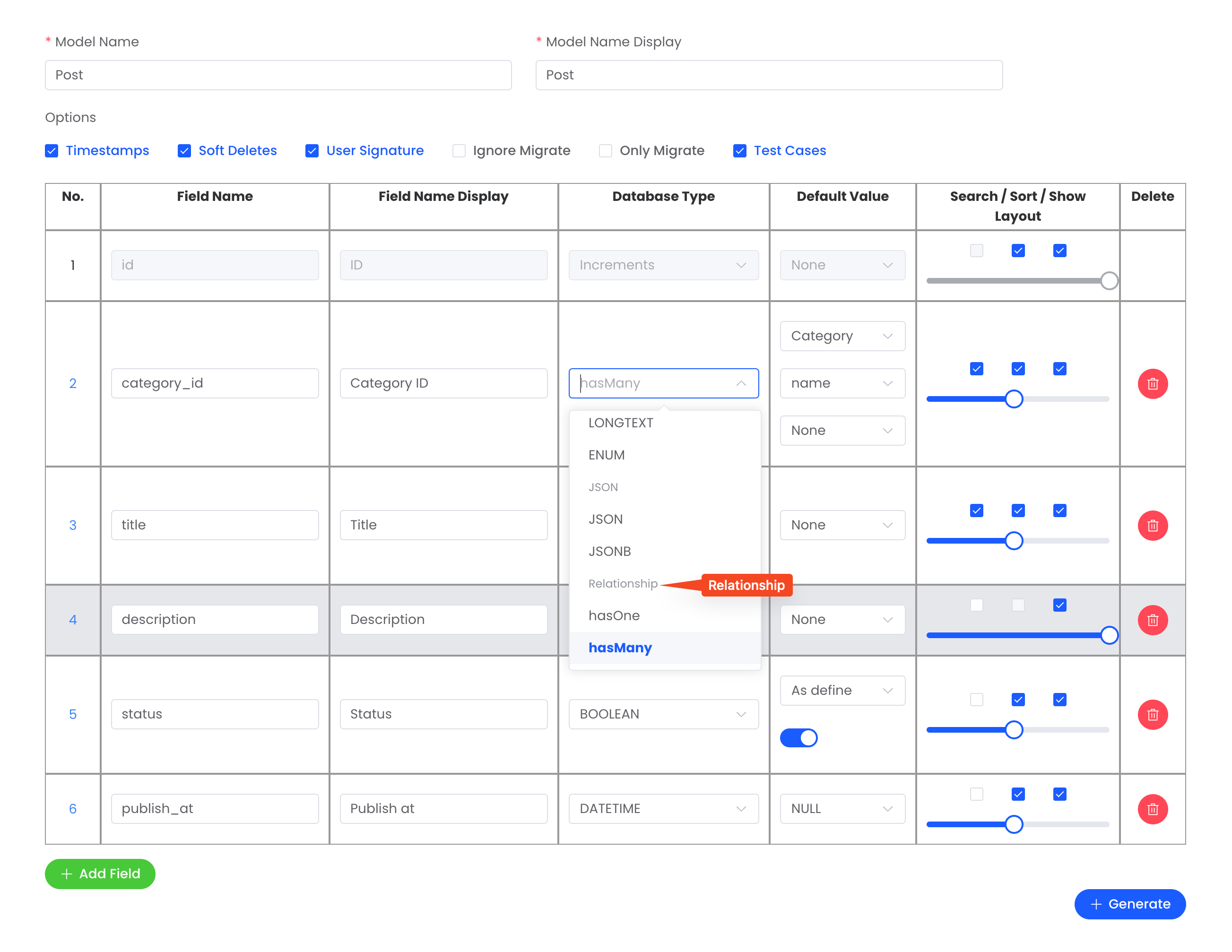
📝 Generate Form
This way just only for hasMany or belongsTo
UI Preview
📝 Relationship Form
This way for all relationship such as: hasOne, hasMany, belongsToMany
UI Preview
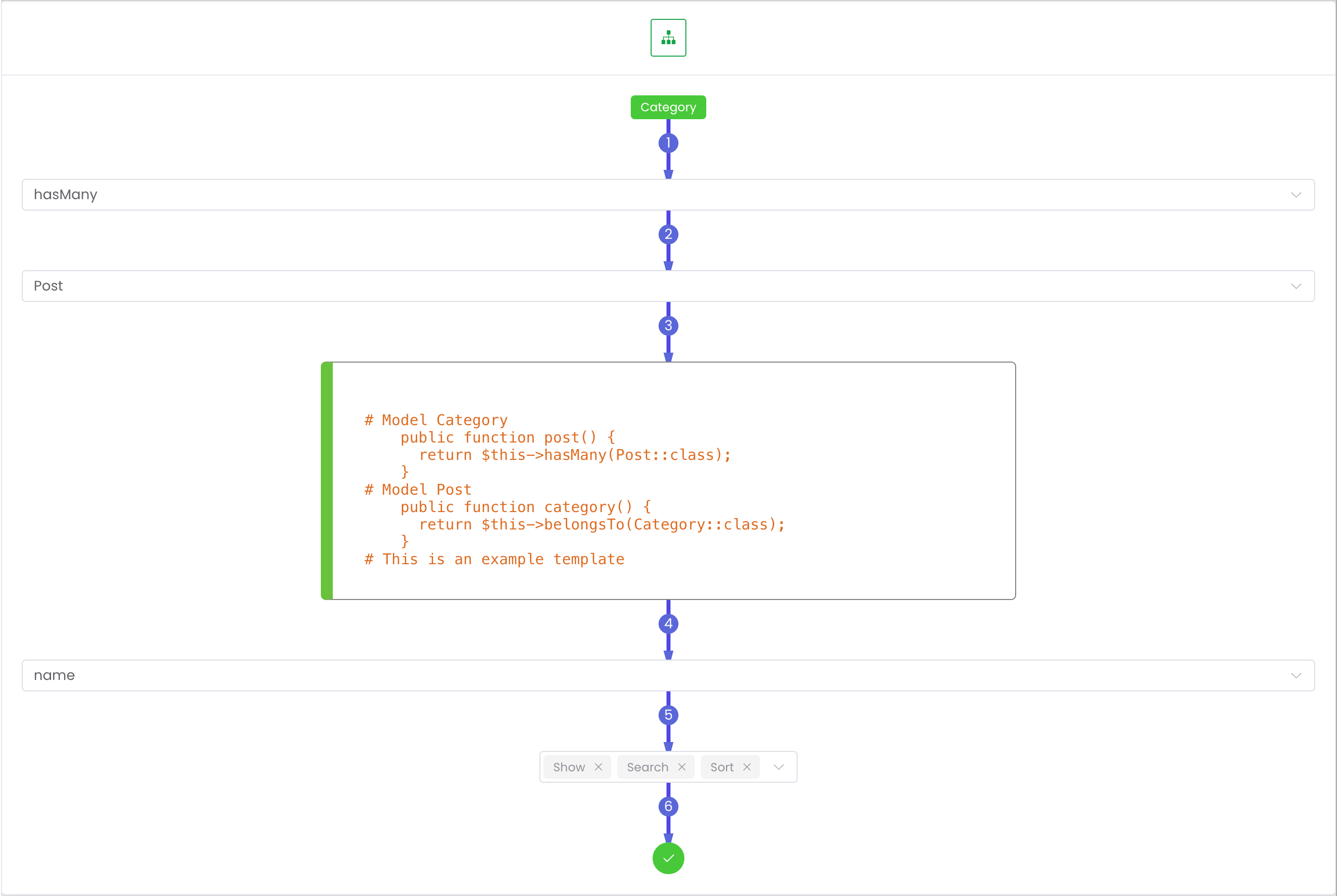
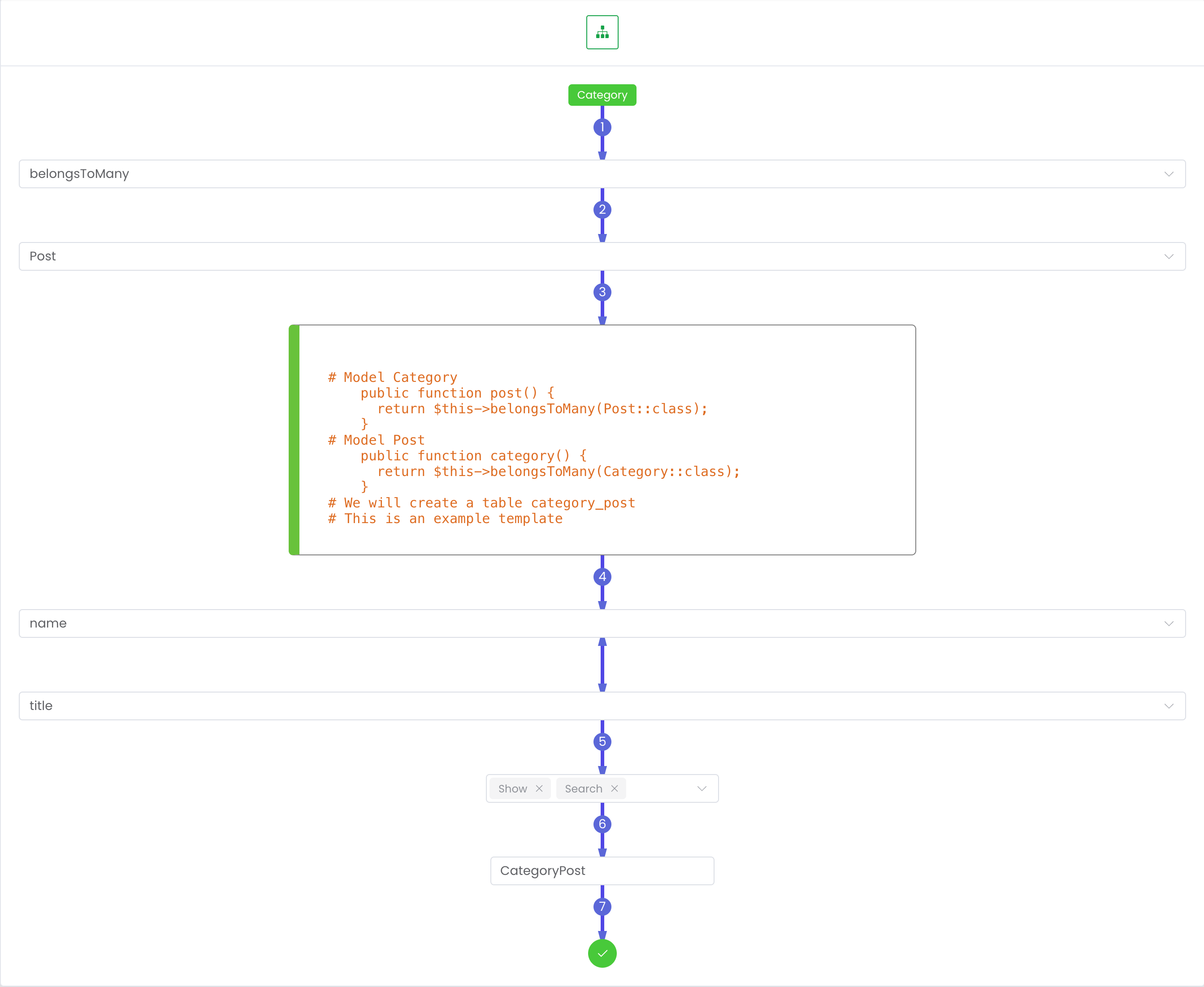
🔄 Many To Many
Many to many will generate pivot table. By default, the pivot table is CategoryPost ({Model1} + {Model2}).
UI Preview
<?php
return new class extends Migration
{
public function up()
{
Schema::create('category_post', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->foreignId('category_id')->index();
$table->foreignId('post_id')->index();
$table->primary(['category_id', 'post_id']);
});
}
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('category_post');
}
};DBML beta
The DBML Interface
LaraJS provides a clean, user-friendly interface for importing DBML content:
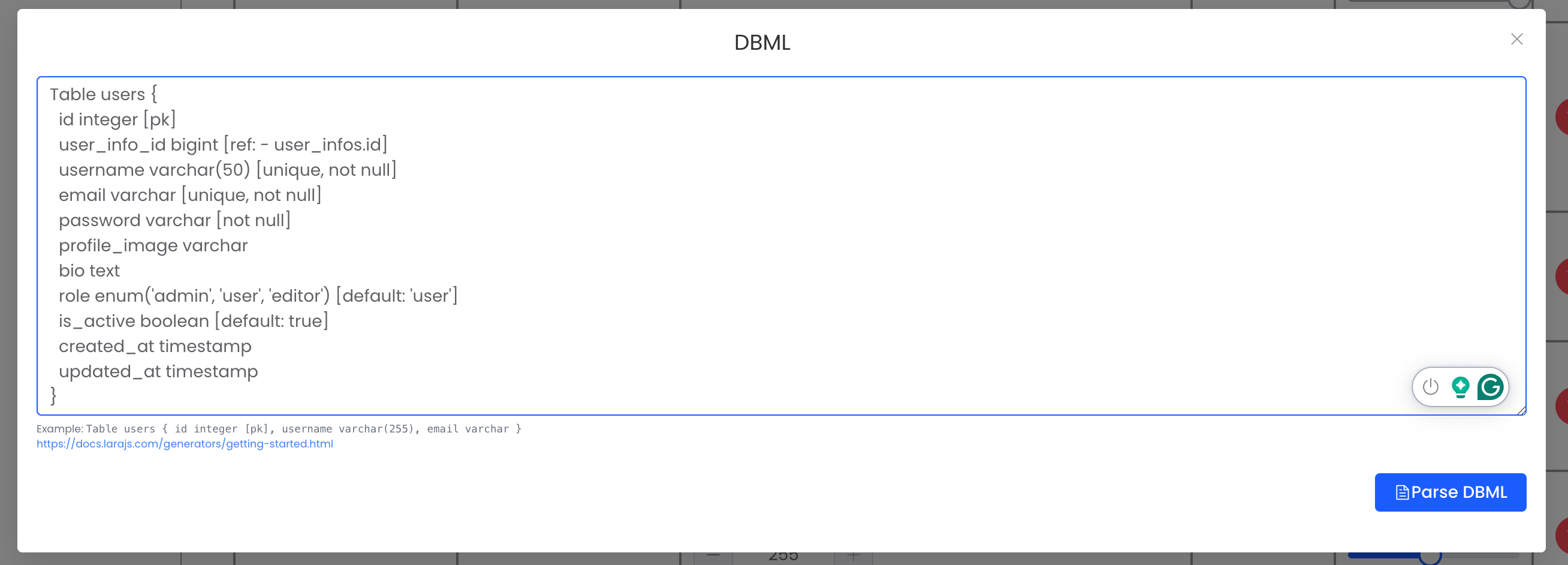
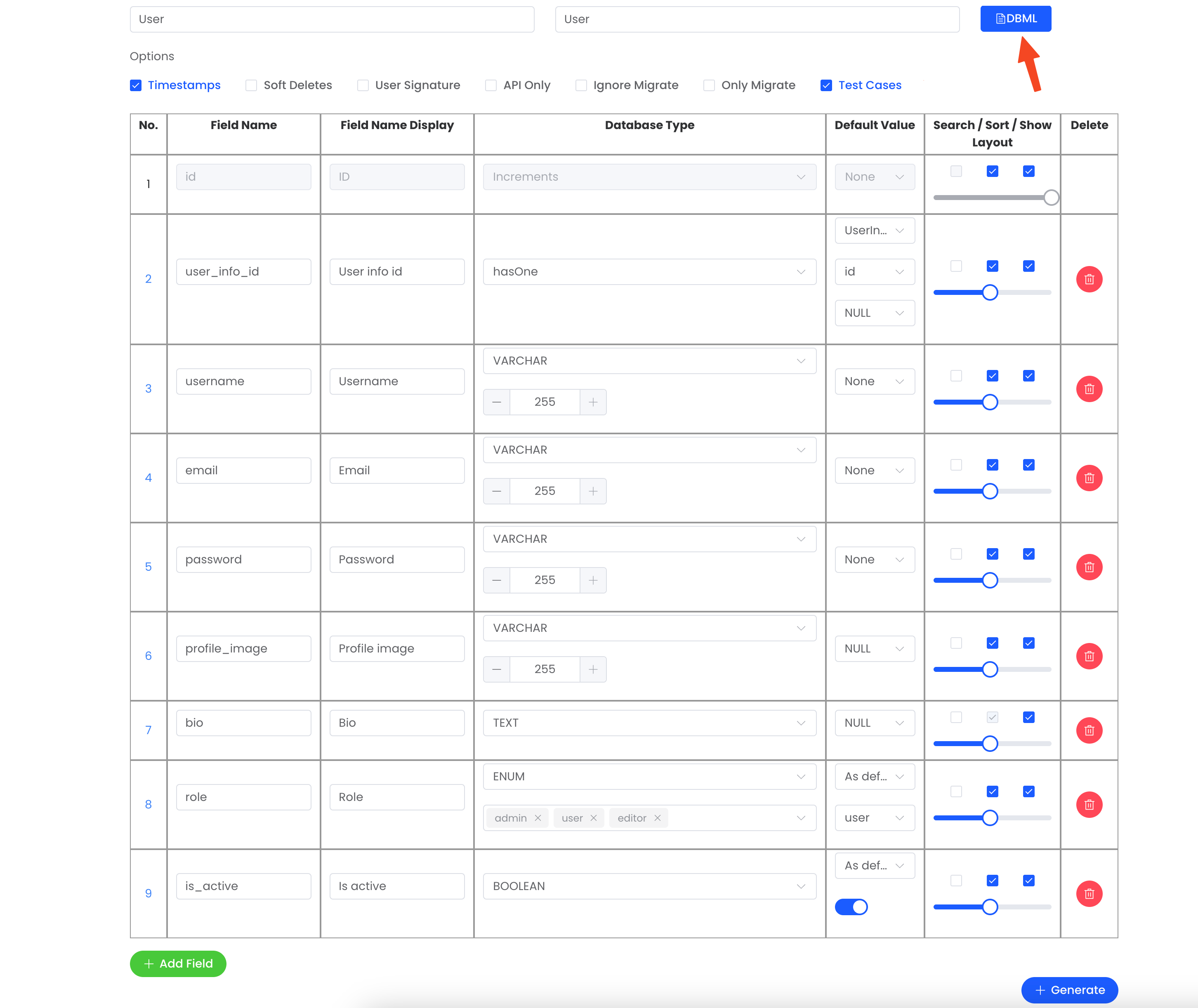
The interface provides:
- A large text area for pasting DBML content
- A reference example to help users understand the syntax
- A link to the official DBML documentation
- A parse button to process the DBML and generate model fields
Complete Type Mapping Reference
The LaraJS DBML parser supports a comprehensive range of database types, mapping them automatically to their corresponding LaraJS database types:
| DBML Type | LaraJS Database Type |
|---|---|
int, integer | INTEGER |
tinyint | TINYINT |
smallint | SMALLINT |
mediumint | MEDIUMINT |
bigint | BIGINT |
float | FLOAT |
double | DOUBLE |
decimal | DECIMAL |
boolean, bool | BOOLEAN |
date | DATE |
datetime | DATETIME |
timestamp | TIMESTAMP |
time | TIME |
year | YEAR |
char | CHAR |
varchar, string | VARCHAR |
text | TEXT |
tinytext | TINYTEXT |
mediumtext | MEDIUMTEXT |
longtext | LONGTEXT |
json | JSON |
jsonb | JSONB |
enum | ENUM |
unsigned int, unsignedint | UNSIGNED INTEGER |
unsigned integer, unsignedinteger | UNSIGNED INTEGER |
unsigned tinyint, unsignedtinyint | UNSIGNED TINYINT |
unsigned smallint, unsignedsmallint | UNSIGNED SMALLINT |
unsigned mediumint, unsignedmediumint | UNSIGNED MEDIUMINT |
unsigned bigint , unsignedbigint | UNSIGNED BIGINT |
Example DBML Syntax:
Table users {
id integer [pk]
user_info_id bigint [ref: - user_infos.id]
username varchar(50) [unique, not null]
email varchar [unique, not null]
password varchar [not null]
profile_image varchar
bio text
role enum('admin', 'user', 'editor') [default: 'user']
is_active boolean [default: true]
created_at timestamp
updated_at timestamp
}Field Attributes and Their Mappings
The DBML parser also handles various field attributes and maps them to appropriate LaraJS configurations:
| DBML Attribute | LaraJS Equivalent |
|---|---|
pk | Identifies the primary key field |
not null | Sets default value to "None" instead of "NULL" |
unique | Enables the "Unique" field option |
index | Enables the "Index" field option |
note: 'text' | Sets a comment in the field options |
comment: 'text' | Sets a comment in the field options |
default: value | Sets default value to "As define" with the value |
ref: > table.column | Creates a "hasMany" relationship to the table |
ref: < table.column | Creates a "hasOne" relationship with the table |
increment | Maps to autoincrement field type |
Relationship Detection
The DBML parser can detect relationships from reference syntax:
[ref: > users.id]detects a hasMany relationship[ref: < comments.post_id]detects a hasOne relationship
Best Practices for DBML Import
For the best results when working with DBML in LaraJS:
- Field Naming: Use snake_case for field names in DBML to maintain consistency with Laravel conventions
- Relationship Definition: Explicitly define relationships using the
ref:syntax to ensure proper relationship detection - Comprehensive Attributes: Include all necessary attributes like unique constraints, defaults, and comments for complete model generation
- Review After Import: Always review the generated fields after import to ensure they meet your requirements
- Incremental Approach: For complex schemas, consider importing tables one at a time rather than all at once
- DBML First Design: Consider using DBML as your initial database design tool before implementation to streamline the development process
Handling Complex Data Types
The DBML parser intelligently handles more complex data types:
- Enum Types: When using
enum('value1', 'value2'), LaraJS automatically creates an ENUM field with the provided values - Length Specification: For types like
varchar(255), the parser correctly sets the length_varchar property - Decimal Precision: For
decimal, LaraJS sets up the appropriate decimal configuration
Troubleshooting Common Issues
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Relationships not detected | Ensure you're using the proper ref: syntax with direction |
| Field types not mapping | Check the type mapping table and use a supported DBML type |
| Default values not applying | Use the format [default: value] with appropriate quotes |
| Unique constraints not applied | Make sure to include [unique] in the field attributes |
| Model name not generated | Check the table name format - it should be Table name {...} |